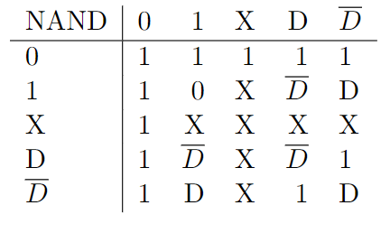
Rules
Roth's D-Alorithm is a 5-value logic consisting of 0, 1, X, D, D'.
The signals D and D' clarify the difference between the normal operation and the fault operation. Therefore, these signals must be passed to the outputs, if present.
D-cube for a stuck-at-1 and a stuck-at-0
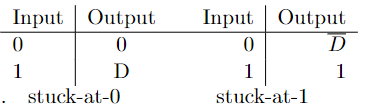
If a stuck-at-1 fault occurs, the input signal of 0 will produce an output signal D', otherwise 0. When the input signal of 1 occurs, it produces in both cases an output signal of 1.
If a stuck-at-0 fault occurs, the input signal of 1 will produce an output signal D, otherwise 1. When the input signal of 0 occurs, it produces in both cases an output signal of 0.
The signal X is used, if the output does not care about the sepcific value of X.
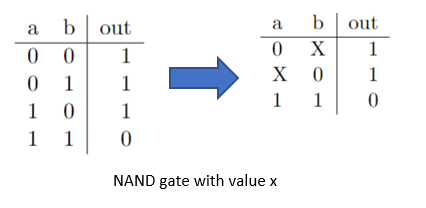
For a NAND gate, the output is logic-0 when both of the inputs are high.
In all other cases the output is a logic-1.
Here you will find the necessary D-cubes for the NAND and NOT gates.